Stripe Size
When you create an hardware RAID array, you must encountered the term stripe size.
For example, an 8-disk RAID 1/0 has a stripe width of 4, with a stripe element size of 64 KB has a stripe size of 256 KB (4 * 64 KB). A 5-disk RAID 5 (4+1) with a 64 KB stripe element size also has a stripe width of 256 KB drive (4 * 64 KB) .
A stripe is the smallest chunk of data within a RAID array that can be addressed. People often also refer to this as granularity or block size. It can be compared to the blocks (logical block addressing - LBA) on conventional hard drives. Most RAID controllers allow the user to define her or his favorite stripe size, because it alters the performance characteristics of a RAID array. Reference
It is important to let the filesystem you use know the underlying RAID array’s stripe size. This is because the filesystem will align its data blocks to the RAID array’s stripe size. This will help to avoid read-modify-write operations, which can be very slow.
For example, when creating a Virtual Disk in a Dell PERC H730P Controller, you can see the stripe element size.
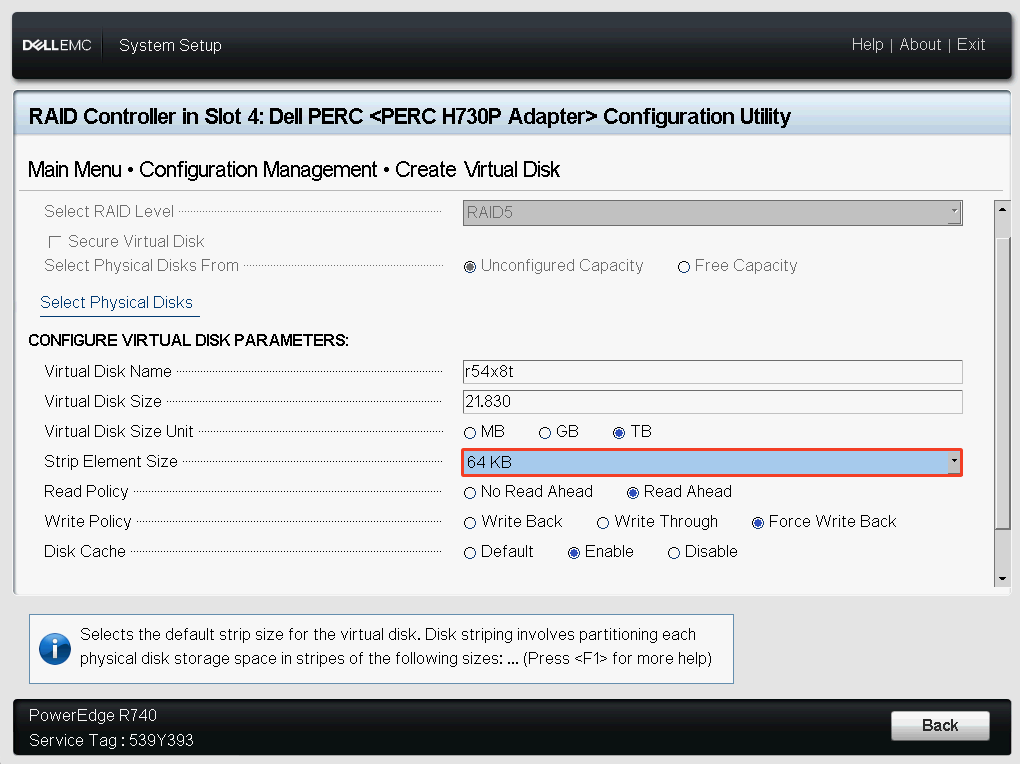
Tune XFS for Hardware RAID
When you format the XFS partition, you can tell XFS about the underlying array info.
For example, I have 4x8T HDDs in RAID 10 with stripe element size of 64 KB. So I have a stripe width of 2 and a stripe size of 128 KB. The corresponding XFS options is sw=2 and su=64k.
| |